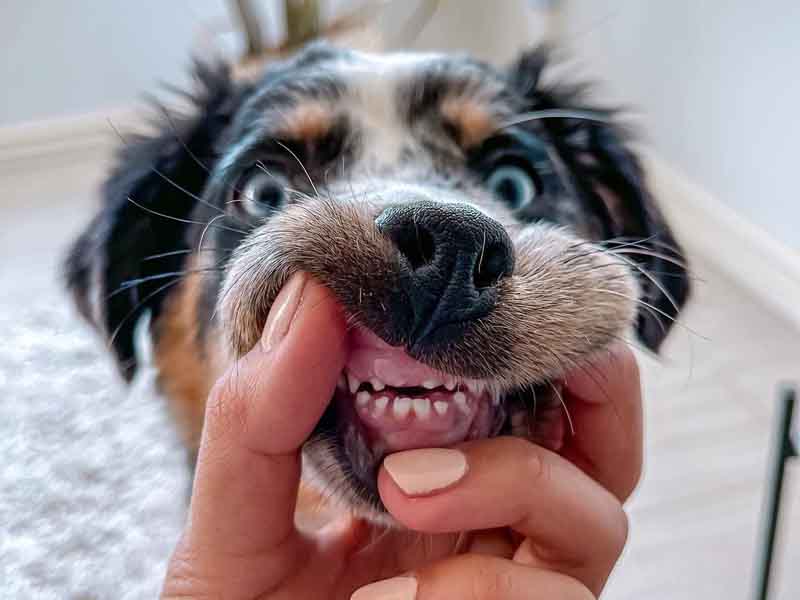
Are you wondering if your dog has retained deciduous teeth? Read this article to know more about them and find out how you should proceed.
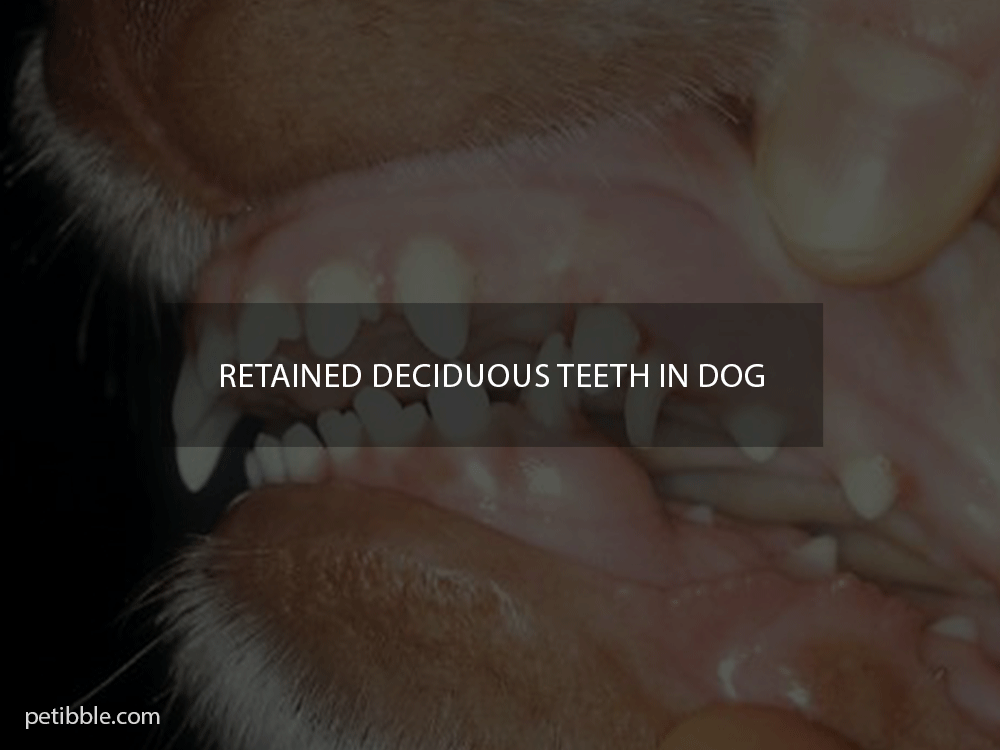
What are retained deciduous or molar teeth?
When your puppy is about 3-4 weeks old, a persistent deciduous tooth will begin to erupt. When your dog is approximately five months old, it will start to fall off. Sometimes they may not normally shed, leading to the retained persistent deciduous tooth.
Canines are more likely to have retained deciduous teeth, but they can also affect deciduous dogs. It can also occur in any breed. Retained deciduous teeth can be caused by genetics or accidents that leave the tooth in the mouth for too long. Gum disease and infection can also be caused by excess plaque and resorption. Canines, however, are more susceptible than human patients.
You may like : everything you need to know about Alaskan Shepherd puppy
How to be sure about retained deciduous teeth?
Retained deciduous teeth can be diagnosed in dogs by a visual examination of their mouths during a physical exam. An x-ray of the dental root can show the relationship between the permanent teeth and the length of the tooth root. The veterinary dentist might recommend surgery if the retained tooth is causing severe pain. Retained deciduous teeth should be removed from dogs to prevent permanent tooth damage. This condition can affect any dog breed, but it is more common in small breeds.
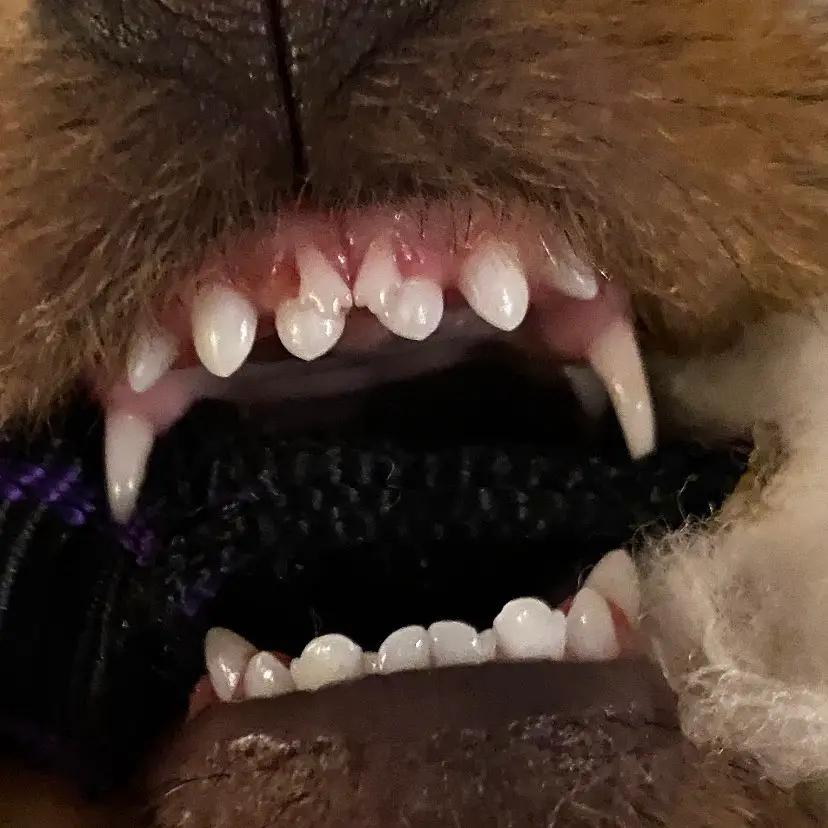
What are the most commonly retained deciduous tooth?
The upper canine tooth is the most common retained deciduous tooth in dogs. It can also be found in incisors and premolars. Retained deciduous teeth that aren’t removed can lead to periodontal disease. This can eventually lead the permanent tooth to be lost. Retained deciduous tooth is a condition that can be detected early. If your puppy is suffering from any of these conditions, a veterinarian will be able to help.
Dogs’ oral health is essential.
It is vital to examine your dog’s oral health at each visit. Retained deciduous teeth can cause periodontal disease and tartar accumulation. An unaligned set of canine teeth can cause problems with chewing and hinder the growth of the maxilla and mandible. You should consult your veterinarian if you notice an abnormal eruption pattern in your dog’s teeth.
You may like: my dog is acting strange after grooming.
It is vital to extract any remaining deciduous teeth.
Retained deciduous teeth are not considered life-threatening. However, they should be taken care of immediately. You should get them out even if they aren’t causing any discomfort or pain to your dog. If a baby tooth has been retained, a vet will examine it and determine if it is a problem. A veterinarian can help you determine if your dog has retained any deciduous teeth. They can cause gum disease and damage surrounding teeth if left in the mouth. Retained deciduous dog and canine teeth problems are best treated by surgical extraction.
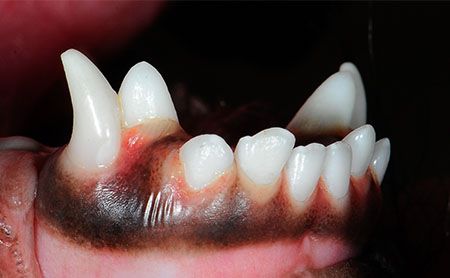
What causes Retained deciduous teeth?
Why your dog retains baby teeth is essential is because adult teeth do not line up with deciduous teeth. Your dog will not look normal if they do not have the proper erupting teeth. You may be able to identify your dog’s primary or secondary teeth if you take a look at their teeth. Dogs with retained deciduous teeth are usually caused by malposition of secondary canine teeth. Root resorption issues can also lead to retained puppy teeth. An impaction can form if the tooth does not erupt. This could lead to your dog losing its other teeth, such as the permanent and second canine molars.
What problems can retain deciduous teeth cause?
Dogs with retained deciduous teeth can pose a variety of problems. They can lead to abnormal bites or crowding. It is possible that the baby tooth is not erupting correctly. It is crucial to have the baby tooth extracted as soon as possible to avoid further complications. Multiple problems can be caused by baby teeth that are not removed. This can lead to periodontal disease and even cause pain. These extra teeth can cause infection if left untreated. Even worse, these extra teeth can disrupt the growth of the rest of the dog’s mouth.
You may like : my dog ate a hair tie, What Should I do?
When should retained deciduous teeth be removed?
Retained baby teeth will eventually fall off when they reach 4-6 months of age. A puppy’s retained teeth will be replaced later with an adult tooth, but the remaining can be
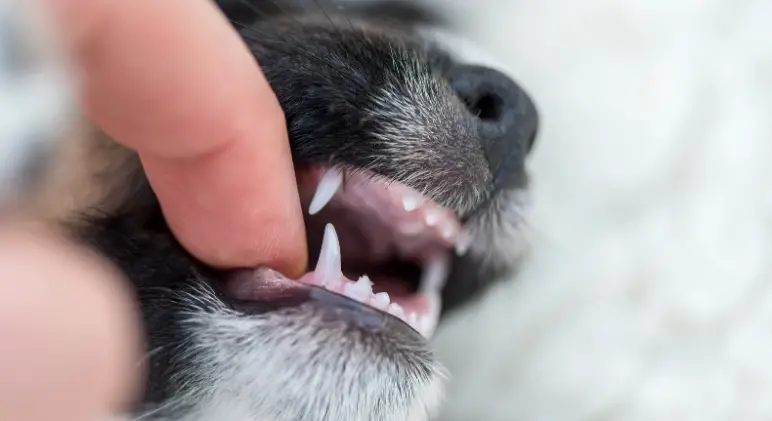

It is best to have them removed.
Retained puppy teeth shouldn’t be left behind and should be extracted as soon as possible. It is crucial to take out your pet’s retained puppy teeth while they are still growing. This will prevent the development of problems with your pet’s teeth that could cause pain. This will contain your puppy from developing adult teeth. It is vital to ensure that your pet’s teeth are healthy and clean for as long as possible. Retained baby teeth can only be removed surgically.
You may like : why are dogs so greedy?
What is the best time for my puppy to remove their retained teeth?
Some dogs tend to keep their baby’s teeth. It is best to get them out when your puppy is six months old. A dental specialist can evaluate your puppy’s oral health and recommend the best course of action. It is crucial to get rid of them as soon as possible. Persistent primary teeth can lead to pain and inflammation and may need to be removed surgically. Although this option is more expensive, it is necessary to protect the roots of the teeth.
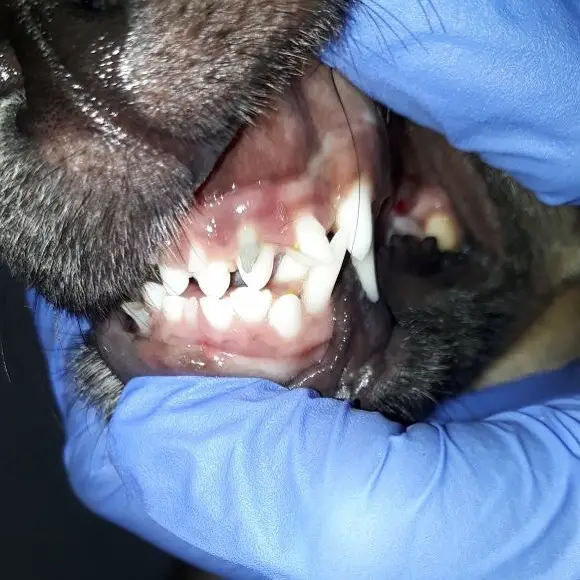
Conclusion.
Retained baby teeth can lead to a host of dental problems, including problems in how your dog bites. A few of these teeth can lead to dental issues in your puppy. These teeth must be removed immediately as they can cause problems with your dog’s adult teeth’ growth. Dogs can have retained baby teeth. They can also cause problems with your dog’s bite and can be very difficult to get out.





